
A rendezvous with Dr. Ashish Dey, Senior Consultant at Sir Ganga Ram Hospital and Honorary Secretary of the Delhi State Chapter of the Association of Surgeons of India, where he explains the infinite advancements and possibilities of robotic surgery.
Robotic surgery has revolutionized healthcare, pushing boundaries since its introduction to India in 2002 with the advent of robotic-assisted procedures using the Intuitive da Vinci system.
Globally, India ranked 10th in annual industrial installations according to the World Robotics Report, 2022.
Looking ahead to 2024, India's healthcare sector anticipates rapid shifts fueled by digital innovations like remote telehealth and advanced robotic surgeries. The country hosts an estimated 24 robotics startups specializing in healthcare.
The appeal and practicality of robotic surgeries lie in their enhanced precision and dexterity, reducing operation times, complications, and improving efficiency. They are minimally invasive, causing less patient discomfort and enabling faster recovery times. Moreover, these surgeries promise revolutionary impacts on healthcare accessibility in remote, disaster-affected, or frontline critical areas.
According to Global Data, a leading data and analytics company, the global market for robotic surgical systems and accessories is set to reach $10 billion by the end of this year, with projections to grow to $15.8 billion by 2030.
Dr. Ashish Dey, Senior Consultant in the Department of Laparoscopic and General Surgery at Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, shares valuable insights on current practices, advancements, and the future potential to transform healthcare delivery, while also addressing limitations, ethical considerations, and challenges associated with this cutting-edge technology.
How did your interest in robotic surgery come about?
Robotic surgery offers increased precision, smaller incisions, is minimally invasive, causes less pain, and involves shorter hospital stays and quicker recovery times. Surgeons benefit from enhanced dexterity and control, eliminating the tremors inherent in human hands, thereby reducing the risks of errors and enhancing outcomes. Robotic surgery is continually evolving and poised to revolutionize healthcare. I chose robotic surgery because it represents the future of surgical procedures, allowing me to offer the best care to my patients. Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, where I practice, supports me fully in utilizing this technology to its fullest potential.
How is AI enhancing robotic surgery?
AI integration into robotic surgery improves the entire spectrum of healthcare by eliminating errors, making decisions based on fed algorithms and protocols, and enhancing preoperative planning, intraoperative decision-making, and postoperative care. AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of real-time patient data, amalgamating it with system-fed data. This machine learning helps surgeons navigate surgical landmarks and planes of dissection more precisely, highlighting crucial anatomical structures that need preservation or avoidance, thereby significantly improving surgical precision.
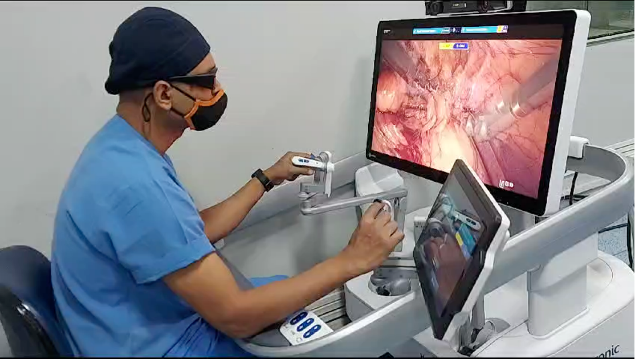
What advantages does robotic surgery offer patients, and how do you address their concerns and fears to encourage their acceptance of this advanced approach?
Robotic surgery offers numerous benefits to patients, as previously mentioned. It is increasingly used in addition to traditional laparoscopic surgeries, neurosurgery (including spine surgeries), cardiac surgeries, vascular surgeries, joint replacements, and more. Correspondingly, patients are becoming more aware of the benefits of robotic surgery through social media and word of mouth. As surgeons, we provide detailed explanations to our patients, informing them of the anticipated improvements in surgical outcomes, cosmesis, and overall safety through robotics. Addressing their apprehensions and fears requires thorough counseling. I ensure ample time for patients to resolve any doubts or insecurities they may have. Interestingly, patients often opt for robotic surgery themselves, underscoring their confidence in its benefits.
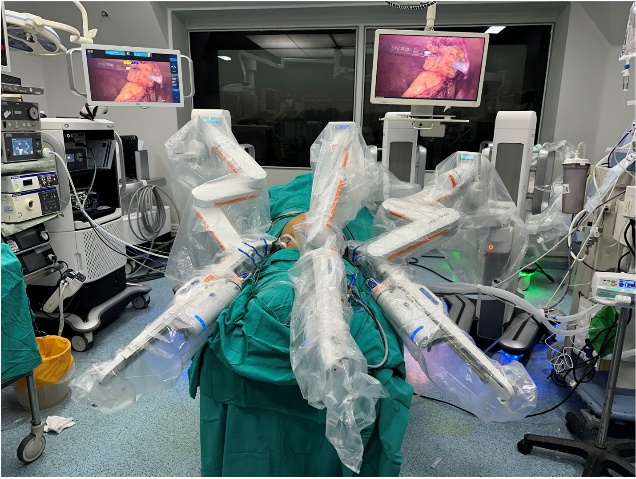
How do you envision co-bots or collaborative robotics influencing surgeries, especially in complex procedures or team-based surgeries involving multiple robotic arms?
Collaborative robots, or co-bots, are increasingly crucial in strategic and complex surgeries. Leveraging AI, these robots work alongside surgeons and other robotic systems to enhance precision and flexibility, assisting in delicate tasks such as fine suturing, tissue alignment, and manipulation. As technology advances, we anticipate more sophisticated robotic systems aiding surgeons in increasingly complex procedures.
Remote surgeries or telesurgeries are frequently discussed these days…
Telesurgery, or remote surgery, is an advanced technology enabling surgeons to perform procedures on patients located in different physical locations and terrains
This innovation holds particular promise in remote areas of India where access to specialized surgical care may be limited. It bridges the gap between patients and skilled healthcare professionals, ensuring timely access to life-saving surgical interventions, even in remote or battlefield stations where surgeons may not be physically present. Telesurgery has the potential to revolutionize healthcare delivery in rural and underserved areas of India, where there is a shortage of medical specialists. However, the main challenges include the substantial costs of setting up such facilities and overcoming regulatory hurdles.
What are the current challenges in robotic surgery, and what breakthroughs do you anticipate in the future to address these challenges?
The main challenges in robotic surgery include the high acquisition and maintenance costs of robotic systems, limited haptic feedback for surgeons, lengthy training requirements, potential technical malfunctions, and concerns about patient safety and outcomes. Solutions lie in continuous training, increasing surgeons' experience with the systems, mentoring, and upskilling, along with technical support such as troubleshooting and maintenance from robotic companies. For example, advancements in haptic feedback using nanotechnology and nanosensors at the instrument tips will enable surgeons to 'feel' tissues to a certain extent, enhancing sensitivity to human anatomical structures. Broader challenges include regulatory issues, ethical considerations, and ensuring equitable utilization of robotic surgery in healthcare. Disparities in access persist due to varying healthcare services and patients' financial capacities, posing challenges to uniform healthcare access.
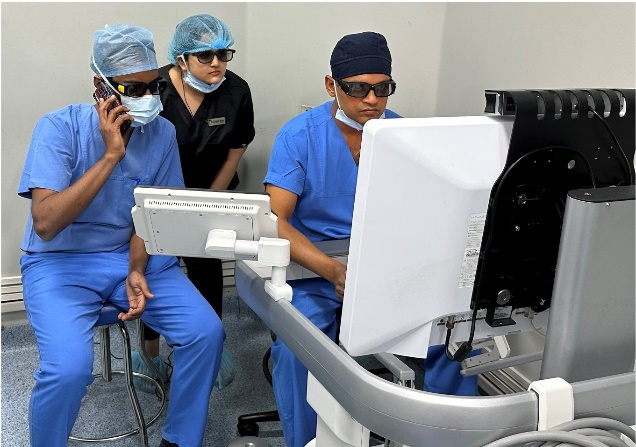
How challenging and frequent is the training required to keep you and your team members updated? Are there specific skills needed to excel in robotic surgeries?
Surgeons require specialized training to operate robotic systems proficiently, understand software interfaces, and interpret visual and non-visual feedback during procedures. Hands-on practice, simulation-based training, and mentorship programs play crucial roles in developing robotic surgical skills. Collaboration between medical institutions, industry partners, and regulatory bodies is essential to establish standardized training protocols and guidelines. This ultimately enhances surgeons' competence and confidence in performing robotic surgeries effectively
What standards or considerations govern robotic surgery systems in India?
Regulations in India are evolving to ensure patient safety and quality care amidst a changing legal and ethical landscape. Government bodies such as the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, the Medical Council of India (MCI), and the National Accreditation Board for Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (NABH) set guidelines for the use of robotic systems in healthcare facilities. These regulations cover aspects such as surgeon training requirements, maintenance and calibration of robotic equipment, informed consent procedures for patients, and reporting adverse events related to robotic procedures. Compliance with these regulations is crucial to promote standardized practices and uphold ethical standards in robotic surgery across India.
What new areas of exploration do you see for robotics, and what challenges accompany each?
Robotic applications hold promise in diverse fields such as Robotic Endoscopy, Robotic Radiosurgery for precise radiation therapy with minimal damage to surrounding tissues, Robotic Microsurgery for delicate procedures like nerve repair or eye surgery, and Robotic Transoral Surgery for accessing difficult-to-reach areas such as head and neck cancers more effectively. These advancements promise more efficient and safer procedures, yet each area presents unique challenges requiring technological innovation and regulatory adaptation.
How much are government and private hospitals investing in surgical robots? How do you view the presence of multiple vendors in this sector?
Both government and private hospitals are making significant investments in surgical robots due to their potential benefits, albeit under different terms and contract agreements. Surgical robots represent a substantial investment for hospitals, involving upfront costs for equipment purchase, as well as ongoing expenses for maintenance, training, and upgrades. The healthcare industry and government agencies recognize the value of investing in surgical robots. Private hospitals invest to maintain competitiveness by attracting patients seeking advanced treatment options, while government hospitals procure robots to enhance their status as flagship institutions in healthcare. Both sectors invest in research, development, and training programs to ensure proficiency in using surgical robots effectively. The presence of multiple vendors offers hospitals various technological capabilities and pricing structures to choose from, with key vendors including Intuitive Surgical (da Vinci Surgical System), Medtronic (HUGO-RAS), and CMR Surgical (Versius), each specializing in different aspects of robotic surgery. Notably, the SSI Mantra, developed indigenously in India by a pioneering cardiac surgeon, offers a more cost-effective alternative, albeit with inherent limitations. Other vendors like TransEnterix (Senhance Surgical System) and Medrobotics (Flex Robotic System) also contribute with innovative solutions tailored for specific surgical needs.
Where do you see India's position in the global landscape of robotics and healthcare?
India has made significant strides in developing and adopting surgical robotic systems in recent years. Indigenous innovations like the SSI Mantra have substantially reduced the cost of surgical robots, making them more accessible to populations in Tier II and III cities. Indian companies and research institutions actively collaborate internationally to leverage expertise in developing cutting-edge robotic technologies tailored to India's healthcare challenges. Government efforts to establish regulatory frameworks ensure safe and efficient use of surgical robots across the country. Initiatives, start-up incubators, and grants are fostering innovation in surgical robotics, reflecting a growing trend in their development and utilization within India's healthcare sector.